E-Mail: sarveshwarreddy131@gmail.com Call Us: +91-9967575529
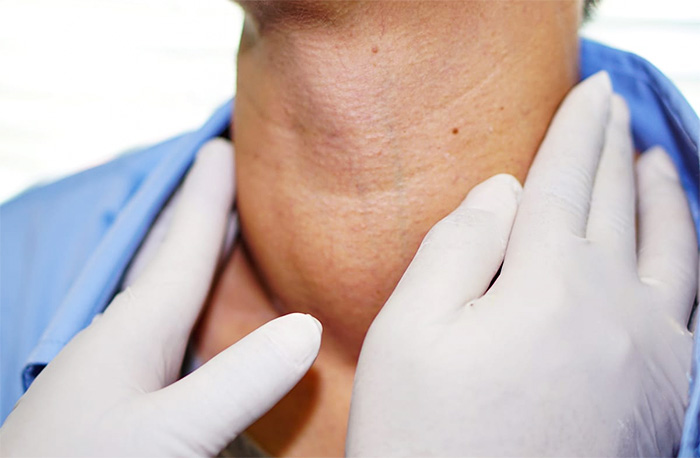
A thyroid lump, also known as a thyroid nodule, is an abnormal growth or swelling in the thyroid gland, located at the base of the neck. These lumps are relatively common and can vary in size, with some being too small to feel, while others may be large enough to cause visible swelling. Most thyroid lumps are benign and do not cause symptoms, but in some cases, they can lead to issues such as difficulty swallowing, breathing problems, or hormonal imbalances. A small percentage of thyroid lumps can be cancerous, making it important to monitor and evaluate any growths in the thyroid.
Thyroid lumps can develop for several reasons, with the most common being benign conditions such as thyroid adenomas, which are non-cancerous growths, and thyroid cysts, which are fluid-filled sacs. Another cause is thyroiditis, an inflammation of the thyroid gland that can result in nodule formation. Iodine deficiency, which affects thyroid hormone production, can also lead to the development of lumps. In rare cases, a thyroid lump may be caused by thyroid cancer, which necessitates further investigation and treatment.
Treatment for a thyroid lump depends on its nature and the symptoms it causes. Benign lumps that do not cause significant symptoms may only require regular monitoring through ultrasound and blood tests. If a lump is causing discomfort or hormonal imbalances, medication to regulate thyroid hormone levels or minimally invasive procedures, such as fine-needle aspiration or radiofrequency ablation, might be recommended. In cases where the lump is large, symptomatic, or suspected to be cancerous, surgical removal of the nodule or even part of the thyroid gland (thyroidectomy) may be necessary.