E-Mail: sarveshwarreddy131@gmail.com Call Us: +91-9967575529
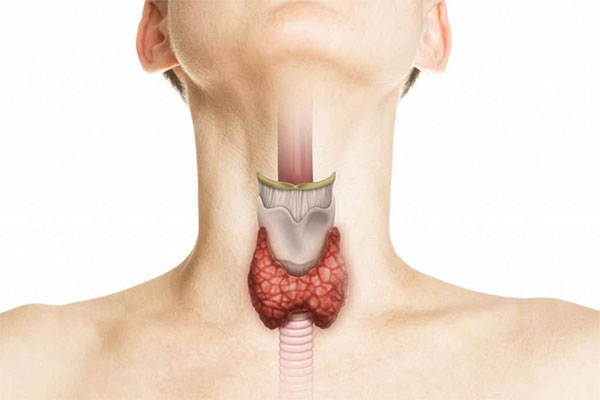
Thyroid disease encompasses a variety of conditions affecting the thyroid gland, a small, butterfly-shaped gland located in the neck. The thyroid plays a critical role in regulating metabolism, energy production, and hormonal balance by producing hormones such as thyroxine (T4) and triiodothyronine (T3). Thyroid diseases can be broadly classified into two categories: hypothyroidism (underactive thyroid) and hyperthyroidism (overactive thyroid). Both conditions can significantly impact overall health, leading to a wide range of symptoms and potential complications if left untreated.
Treatment for thyroid disease depends on the specific condition. Hypothyroidism is usually treated with synthetic thyroid hormone replacement (levothyroxine) to normalize hormone levels. Hyperthyroidism may be managed with antithyroid medications (like methimazole), radioactive iodine therapy, or surgery to remove part or all of the thyroid gland. Lifestyle modifications, such as dietary adjustments and regular monitoring of thyroid hormone levels, are also crucial components of managing thyroid disease.