E-Mail: sarveshwarreddy131@gmail.com Call Us: +91-9967575529
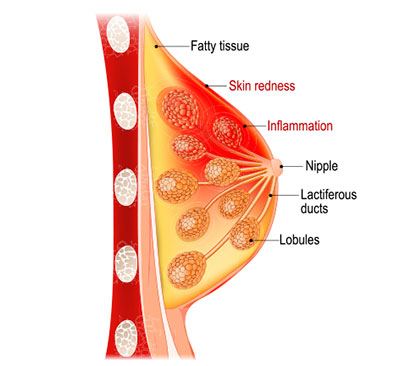
A breast abscess is a localized collection of pus within the breast tissue, typically resulting from an infection. It is most commonly seen in women who are breastfeeding, but it can also occur in non-lactating women due to other factors. The abscess forms when bacteria, usually Staphylococcus aureus, enter the breast tissue through cracked or damaged nipples, leading to an infection that the body walls off, creating a pocket of pus.
Treatment for a breast abscess typically involves draining the abscess to remove the pus, which can be done through needle aspiration or surgical incision and drainage. Antibiotics are often prescribed to treat the underlying infection and prevent recurrence. In some cases, pain relief medications and warm compresses may be used to alleviate symptoms. If the abscess is related to breastfeeding, continuing to breastfeed or pump from the affected breast is encouraged, as it can help clear the infection and prevent milk stasis.