E-Mail: sarveshwarreddy131@gmail.com Call Us: +91-9967575529
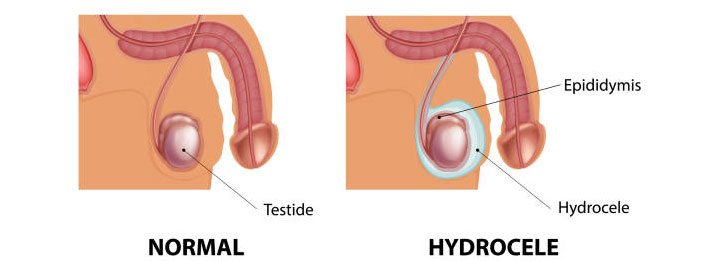
A hydrocele is a fluid-filled sac that forms around the testicle, causing swelling in the scrotum. It is often painless and may develop on one or both sides. Hydroceles can occur in newborns or adults, and while they are usually benign, they may cause discomfort or become a cosmetic concern.
In newborns, a hydrocele often results from a failure of the processus vaginalis, a channel through which the testicles descend during fetal development, to close properly. In adults, hydroceles can arise due to injury, inflammation, or infection of the testicle or surrounding structures. They can also be associated with conditions such as testicular tumors or epididymitis.
Treatment for a hydrocele may not be necessary if it is asymptomatic and not causing problems. However, if the hydrocele causes discomfort or complications, surgical intervention is typically recommended. The most common procedure is hydrocelectomy, where the surgeon removes the fluid-filled sac. In some cases, aspiration of the fluid may be performed, but this approach has a higher risk of recurrence.