E-Mail: sarveshwarreddy131@gmail.com Call Us: +91-9967575529
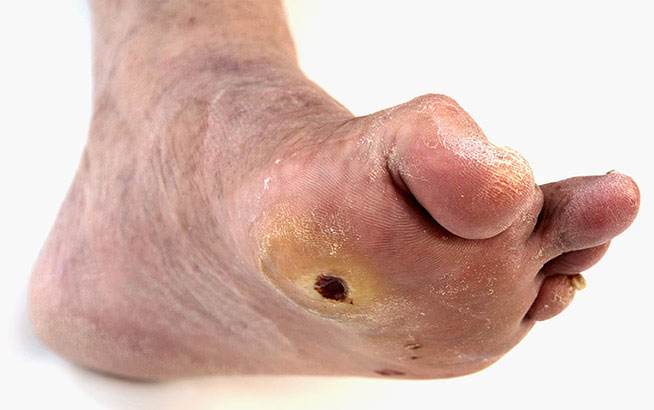
A Diabetic Foot Ulcer is an open sore or wound that commonly occurs on the bottom of the foot in people with diabetes. These ulcers can develop due to a combination of factors associated with diabetes, such as poor circulation and nerve damage (neuropathy), leading to a reduced ability to feel pain or pressure and an impaired healing process. If not properly managed, DFUs can lead to serious complications, including infection, gangrene, and even amputation.
Treatment for a Diabetic Foot Ulcer involves comprehensive wound care, including regular cleaning and dressing of the ulcer, offloading pressure from the affected area with special footwear or casts, and controlling blood sugar levels to enhance healing. Antibiotics may be prescribed to treat or prevent infection. Advanced therapies such as growth factors, skin substitutes, or hyperbaric oxygen therapy can be used in severe cases to promote healing. In cases where the ulcer does not heal or leads to severe infection, surgical intervention may be necessary to remove dead tissue or, in extreme cases, amputate the affected part of the foot to prevent further complications.