E-Mail: sarveshwarreddy131@gmail.com Call Us: +91-9967575529
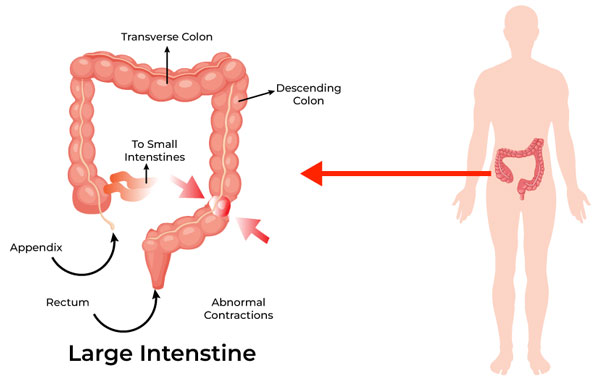
Irritable Bowel Disease is a group of chronic inflammatory conditions of the gastrointestinal (GI) tract, with the two main types being Crohn's disease and ulcerative colitis. IBD is characterized by periods of flare-ups and remission, where the immune system mistakenly attacks the GI tract, leading to inflammation and damage. The exact cause is unknown, but it involves a combination of genetic, environmental, and immune factors.
Treatment for IBD focuses on reducing inflammation, managing symptoms, and maintaining remission. It typically includes anti-inflammatory medications like aminosalicylates and corticosteroids, immunosuppressants to control the immune response, and biologic therapies targeting specific pathways in the inflammatory process. Antibiotics may be used to treat infections, and surgery might be necessary to remove damaged sections of the GI tract in severe cases. Additionally, lifestyle changes, including dietary adjustments, stress management, and regular exercise, play a crucial role in managing IBD and preventing flare-ups.